Dr. Rajagopal Dispenses Needed Medicines and a Healthy Dose of Respect.

Pallium India
After a meeting with CFHI’s Founder, Dr. Evaleen Jones at Stanford University, Dr. Rajagopal (Dr. Raj), the Founder of Pallium India agreed to become one of CFHI’s newest partners in India. CFHI India Coordinator, Ms. Hema Pandey, and I had the privilege of spending three days with him in Trivandrum, Southern India as we work to develop a CFHI Global Health Immersion Program exploring Palliative Care.
As the monsoon season takes its time to come to a close, the beautiful, lush countryside around Trivandrum in Kerala –Southern India is as calming as the  presence of Dr. Raj to his patients. We were given the great privilege of being allowed to shadow Dr. Raj during a day of home visits to various patients of Pallium India, the nonprofit he founded.
presence of Dr. Raj to his patients. We were given the great privilege of being allowed to shadow Dr. Raj during a day of home visits to various patients of Pallium India, the nonprofit he founded.
Who is Dr. Rajagopal
Dr. Raj is responsible for beginning the palliative care movement in India. He tells me that while the goal of palliative care might be the same in India as it is in England, where the modern hospice movement was started, the implementation is different. Dr. Raj feels that to simply pick up and transplant palliative care as it has been developed in the West can inadvertently have consequences that cause more suffering –when the main goal of palliative care is to reduce suffering. Dr, Raj is indeed a unique individual; he is both a visionary and a worker in the trenches. To follow him for a day doing home visits was inspiring. It was also a primer in how to do this kind of patient care.
Dr. Raj pointed out to me the four domains of patient care that were outlined by Cicely Saunders, the founder of the modern hospice movement. The four interlocking domains are Physical, Emotional, Social, and Spiritual. It is certainly a tall order for anyone to provide such comprehensive care, and to do it in low resource settings is even more challenging.
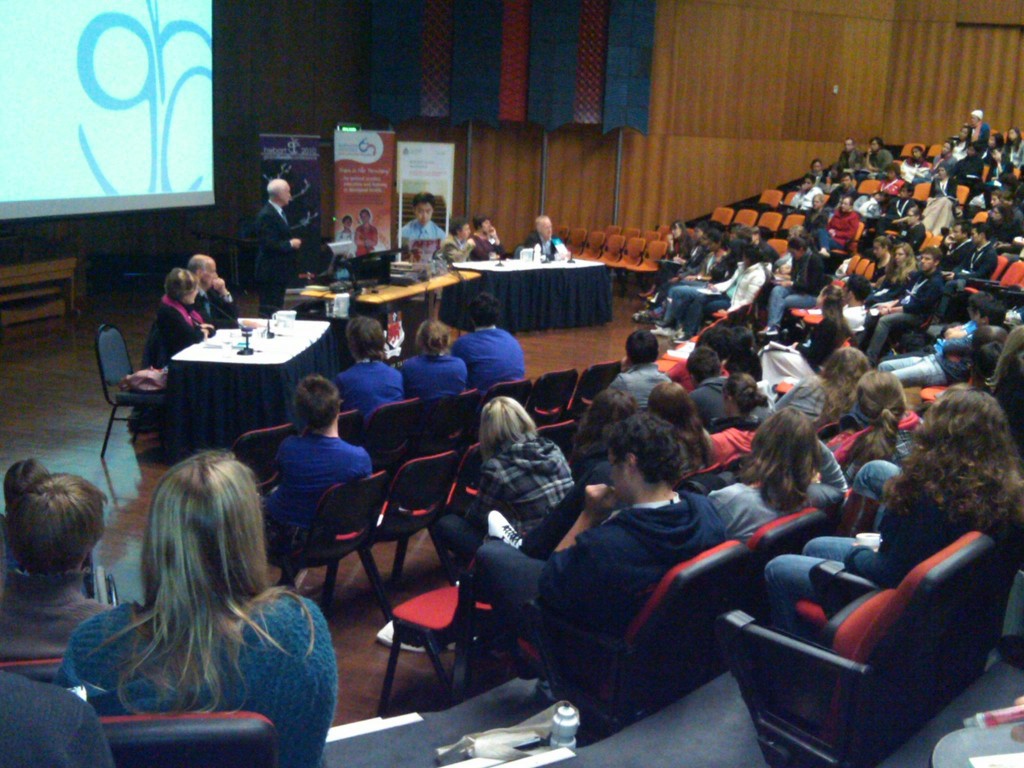
A Day in the Life– Implementing Palliative Care in India
As we drove into some of the poorest communities in Southern India, Dr. Raj and his team, a nurse, a social worker, and a driver went about their routine. Patient files are reviewed as we travel in the van. The size of the patient files is notable. After Dr. Raj read the file a bit, he begins to tell us the context of the family we are about to see. We get a succinct yet

Ms. Hema and Dr. Raj on home visits
thorough description of the family composition and history. The level of detail is impressive and we even had a few questions about the family that Dr. Raj answered from the record. I asked him when he last saw the family and he said that this was his first visit to them. There are three other teams conducting home visits and so the family has been seen by the other teams in the past. It is amazing to see the level of detail that is recorded from the home visit. From these notes, other services from nutrition, to physical therapy, to social work are provided –all driven initially from the teams’ weekly or fortnightly visits.
As we arrive, Dr. Raj gives warm and respectful greetings. He makes use of his reading of the chart right away to let the family know that he is up to speed on the situation even though this is his first time seeing them. Telling and retelling the story can be a help, at times, for a family but to have to do it with every healthcare worker that shows up, can become a burden.
In the home visit, Dr. Raj is totally in his element. Calm, positive, and respectful, he has a way of making the patient and the family feel that he has all the time in the world to spend with them –they have no idea that he has six more home visits to do. His careful touch, his undivided attention, his deep listening, his affirming comments are all the epitome of what a home visit should be. He listens and draws

Dr. Raj conducting a home visit, Trivandrum Southern India
out information to help him tweak the treatment plan based on what has happened since the previous home visit. As he leaves, he has given not only some medicines and ordered some more physical therapy but he has also given the family and the patient dignity, respect, and acknowledgment through his manner, his interactions, and his presence.
And, of course, as we make it back to the van, it’s time for Dr. Raj to write page after page of notes so the follow-up treatments can be done and so the next home visitor can pick up right where he left off.

















 Health Immersion Programs
Health Immersion Programs